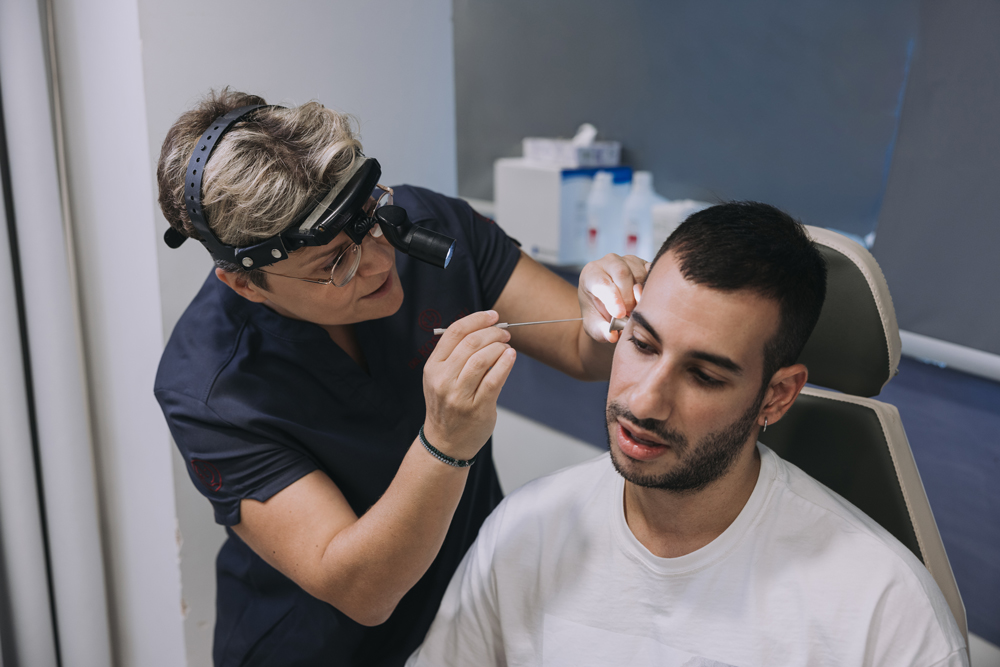
Ear
Why Ear Health Matters
Our hearing and balance rely on a highly sensitive and complex organ: the ear. Even seemingly “simple” issues — such as a blocked ear, frequent infections, or tinnitus — can affect daily life, children’s speech development, communication, sleep, and social interaction. Early evaluation by an ENT specialist is essential to prevent permanent damage and restore hearing.
Dr. Kosmidou’s Approach to Otology
As an ENT Surgeon and Director of the ENT – Head & Neck Surgery Center at the Mediterranean Hospital of Cyprus, Dr. Panagiota Kosmidou combines advanced clinical experience with academic expertise in hearing. Her doctoral research focused on the early detection of hearing loss in newborns, which greatly informs her approach to pediatric otology and preventive audiological care. At her clinic, patients receive personalised care ranging from conservative management and monitoring to advanced microsurgical ear procedures.
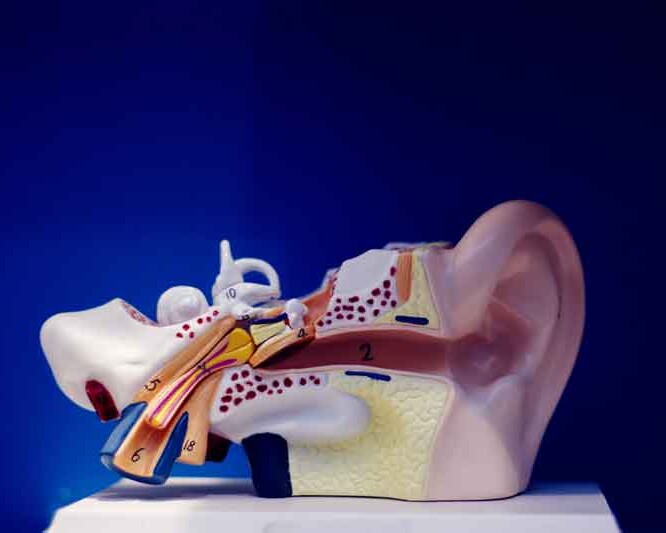
Ear Anatomy & Function Explained Simply
The ear is divided into three parts:
- Outer ear: Pinna & ear canal – collect sound.
- Middle ear: Eardrum & ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) – transmit vibrations.
- Inner ear: Cochlea (hearing) & labyrinth (balance).
When something disrupts this chain—such as an infection, fluid, trauma, or degenerative condition—hearing loss, pain, or dizziness can occur. Accurate diagnosis identifies whether the problem lies in the outer, middle, or inner ear and guides the appropriate treatment.
Symptoms That Require Medical Evaluation
If you notice one or more of the following, an evaluation is recommended:
- Recurrent ear pain
- Blocked ear / feeling of pressure
- Fluid or pus discharge
- Hearing loss (sudden or gradual)
- Tinnitus (ringing or buzzing)
- Dizziness or vertigo
- Child with fever pulling at the ear
- Delayed speech development in a child
Important: Sudden hearing loss requires immediate medical attention.

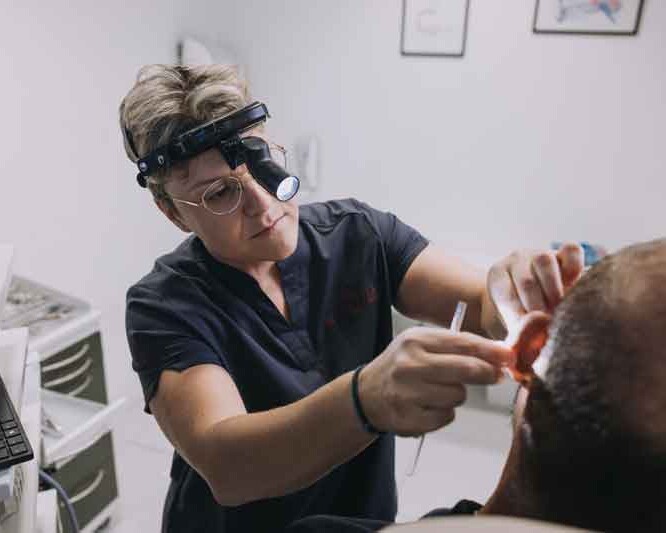
Non-Surgical Conditions & Conservative Management
In many cases, proper medication or supportive therapy can resolve or control the problem without surgery.
- Otitis (Acute / Chronic): Infection of the middle or outer ear, causing pain, fever, discharge, or hearing loss. Treatment may include antibiotics (when indicated), topical drops, allergy management, or monitoring.
- Otitis Media with Effusion (Fluid in the Middle Ear): Common in children after infections or due to enlarged adenoids. Can affect hearing and speech development. Monitored carefully, but persistent cases may require ear tube placement.
- Earwax Impaction: A common cause of blockage. Removed via gentle suction or irrigation; never attempt aggressive removal at home.
- Tinnitus: May be related to hearing loss, noise exposure, otosclerosis, or other factors. Management is individualized: hearing assessment, risk factor modification, therapeutic approaches, or intratympanic injections in select cases.
- Vertigo / Vestibular Disorders: Evaluation for Meniere’s disease, benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), viral labyrinthitis, or other causes.
- Otosclerosis: Progressive mixed hearing loss due to stapes fixation. Requires specialized assessment; surgical options may be considered on a case-by-case basis.
Otology & Audiology Surgical Procedures
Dr. Kosmidou performs a wide range of otologic surgical procedures aimed at restoring hearing, relieving pain or infections, and preventing complications.
- Removal of Foreign Bodies from the Ear Canal: Common in children and adults. Removed using microsurgical instruments under direct visualization to avoid injury.
- Surgical Repair of Ear Trauma: For injuries, torn earlobes (e.g., from earrings), or tissue loss. Reconstructive techniques aim for optimal functional and aesthetic outcomes.
- Tympanostomy (Myringotomy): Small incision in the eardrum to drain fluid in acute or effusive otitis media.
- Ventilation Tube Placement (“Ear Tubes”): Tiny tubes keep the eardrum opening patent to ventilate the middle ear and prevent fluid recurrence. Especially beneficial for children with recurrent or effusive otitis media.
- Tympanoplasty: Surgical repair of eardrum perforations and, when needed, reconstruction of the ossicular chain to improve hearing and prevent infections.
- Intratympanic Injections: Administration of medication (e.g., corticosteroids) directly into the middle ear for tinnitus or sudden hearing loss when indicated.
Tinnitus & Sudden Hearing Loss
Tinnitus can be occasional or chronic and requires thorough evaluation. In certain cases, specialised treatments or intratympanic injections may be applied. Sudden hearing loss is a medical emergency: the sooner treatment begins, the better the prognosis.
Hearing Assessment – What It Involves
Depending on age and specific concerns, the following assessments may be used:
- Otoscopy & Ear Microscopy
- Pure Tone Audiometry
- Tympanometry – evaluates eardrum mobility and middle ear pressure
- Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) / Evoked Potentials – useful for infants and complex cases
- Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE) – newborn hearing screening
- Vestibular Testing – for dizziness or vertigo
A comprehensive diagnosis guides the appropriate treatment, whether conservative or surgical.
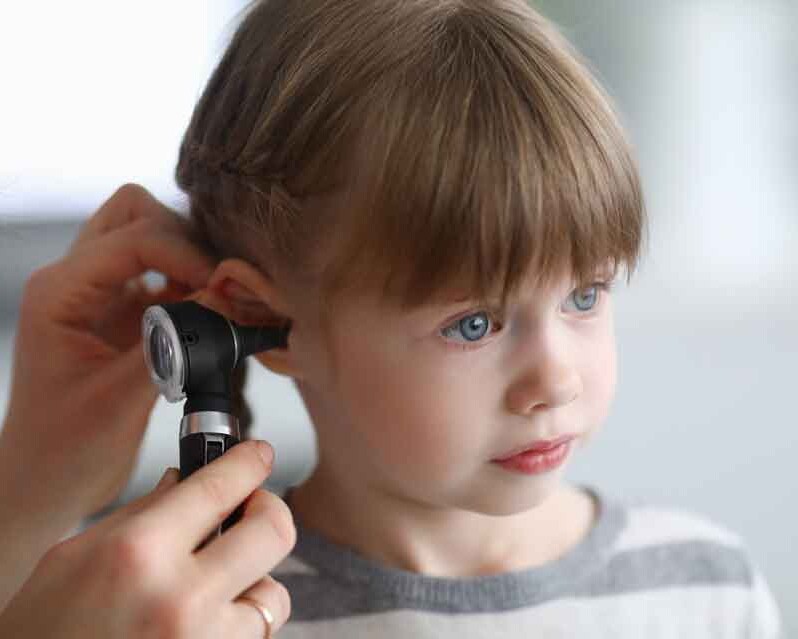


Pediatric Otology & Newborn Hearing Screening
Dr. Kosmidou has a strong academic background in early detection of hearing loss in newborns, the focus of her doctoral research. This expertise translates into meticulous pediatric care, including:
- Hearing screening for newborns and infants
- Monitoring children with recurrent ear infections
- Assessing speech or language delays related to hearing
- Collaboration with pediatricians and speech therapists when needed
Early diagnosis of hearing loss in children supports speech development, learning, and social integration.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often do children get ear infections?
Very frequently at a young age, especially after viral illnesses or due to enlarged adenoids.
Do all children need ear tubes?
No. Tubes are placed when fluid persists in the middle ear or when recurrent infections affect hearing.
Can tinnitus be treated?
It depends on the cause. Evaluation is necessary. Various therapeutic and supportive approaches are available.
Does tympanoplasty hurt?
The procedure is performed under anesthesia. Postoperative pain is usually mild, temporary, and manageable.
When to Schedule a Visit
Contact the clinic if you experience:
- Frequent ear infections (in yourself or your child)
- Hearing loss or sudden “blocked” sensation in the ear
- Persistent tinnitus
- Ear or eardrum injury
- Need for specialized surgical repair
Reach out to schedule an evaluation and receive a personalized treatment plan.
